Introduction
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14, which focuses on life below water, plays a pivotal role in preserving marine ecosystems and promoting ocean conservation. In Palawan, the Philippines, this global objective is crucial due to its rich marine biodiversity. With stunning coral reefs, abundant marine life, and crystal-clear waters, Palawan is a key location for the implementation of SDG 14.
This article explores how SDG 14 in Palawan is contributing to the achievement and how local initiatives and efforts can empower marine conservation for future generations.
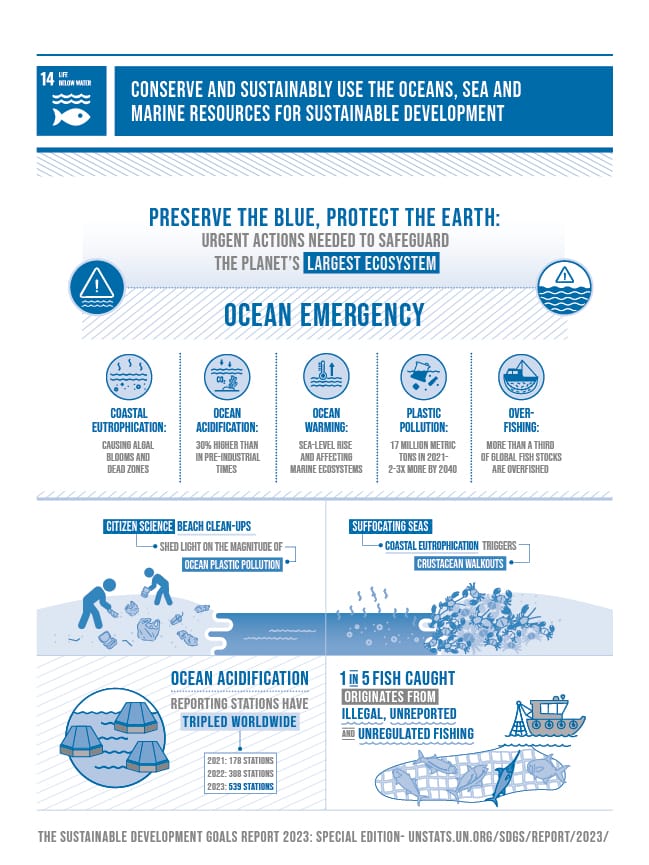
Table of Contents
1. SDG 14 in Palawan
SDG 14, part of the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources. It includes efforts to prevent marine pollution, protect marine ecosystems, and manage coastal areas responsibly. SDG 14 advocates for the conservation of marine biodiversity, ensuring sustainable fishing practices, and protecting the health of oceans globally.
2. Palawan: A Marine Sanctuary
Palawan, often referred to as the “last frontier” of the Philippines, is home to some of the world’s most pristine marine environments. The island’s protected areas, such as the Tubbataha Reefs Natural Park and El Nido, are critical to marine biodiversity and support the goals of SDG 14. The rich coral reefs and abundant marine life, including sea turtles, sharks, and various fish species, make it an important area for marine conservation.
In 2015, the Tubbataha Reefs, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was designated as a protected area. The reefs are home to some of the most diverse marine ecosystems in the world. These efforts contribute significantly to the achievement of SDG 14 in Palawan.
3. Local Initiatives in Palawan: Empowering Marine Conservation
One of the key aspects of achieving SDG 14 is raising awareness and involving local communities in marine conservation efforts. In Palawan, local organizations, communities, and government agencies are actively working to protect marine life.
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs):
Palawan has implemented numerous MPAs, including the recently established ones in Coron and El Nido. These areas are vital for protecting coral reefs, fish nurseries, and critical marine habitats. MPAs help limit destructive activities, such as illegal fishing and pollution, and contribute to the regeneration of marine life.
Coral Restoration Projects:
Coral reefs are under threat from climate change, overfishing, and pollution. In response, several organizations in Palawan are spearheading coral restoration projects. These efforts include transplanting coral fragments and using innovative methods to regenerate damaged reefs. The success of these projects is crucial to achieving SDG 14 in the region.
Community Empowerment:
Local communities are crucial in marine conservation efforts. Palawan’s coastal communities are involved in various programs that focus on sustainable livelihoods, reducing plastic waste, and implementing eco-tourism practices. By empowering locals, these initiatives ensure that conservation is integrated into everyday life, helping to build a sustainable future for both people and marine ecosystems.
4. The Role of Tourism in SDG 14 in Palawan
Tourism plays a significant role in Palawan’s economy, but it also has a responsibility to contribute to SDG 14. Sustainable tourism practices, such as eco-friendly tours and responsible fishing activities, are increasingly becoming popular among travelers. The region has started promoting responsible tourism by educating visitors on the importance of marine conservation and encouraging eco-conscious behavior.
By supporting sustainable tourism, Palawan’s marine resources can be protected while still generating income for local communities. This balance is crucial for achieving the targets of SDG 14.
5. Challenges to Achieving SDG 14 in Palawan
Despite the progress made, there are still significant challenges to achieving SDG 14 in Palawan. Issues such as illegal fishing, waste management, and climate change pose ongoing threats to the region’s marine ecosystems.
To address these challenges, it is essential to strengthen local enforcement, raise awareness, and ensure that businesses and visitors adhere to sustainable practices. The continued collaboration of local government units, NGOs, and the private sector will be vital in overcoming these hurdles.
6. Conclusion: Empowering the Future of Marine Conservation
Palawan’s efforts toward achieving SDG 14 showcase the importance of community involvement, local initiatives, and sustainable tourism in marine conservation. By empowering local communities and supporting conservation projects, Palawan is making significant strides toward preserving its rich marine ecosystems for future generations.
However, achieving SDG 14 in Palawan requires the ongoing collective effort of governments, businesses, local communities, and visitors. As we continue to work toward a sustainable future, Palawan’s commitment to SDG 14 will serve as an example for other regions around the world to follow in protecting and preserving our oceans and marine life.

